Describe How New Nucleotides Are Added During Dna Replication.
Describe the structure of DNA. As the strands are antiparallel with opposing polarity and since DNA polymerases can only synthesize DNA in the 5 to 3 direction only one strand is continuously synthesized.
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
DNA polymerase is a type of enzyme that is helpful to make copies of the DNA in the form of Nucleic acid molecules.
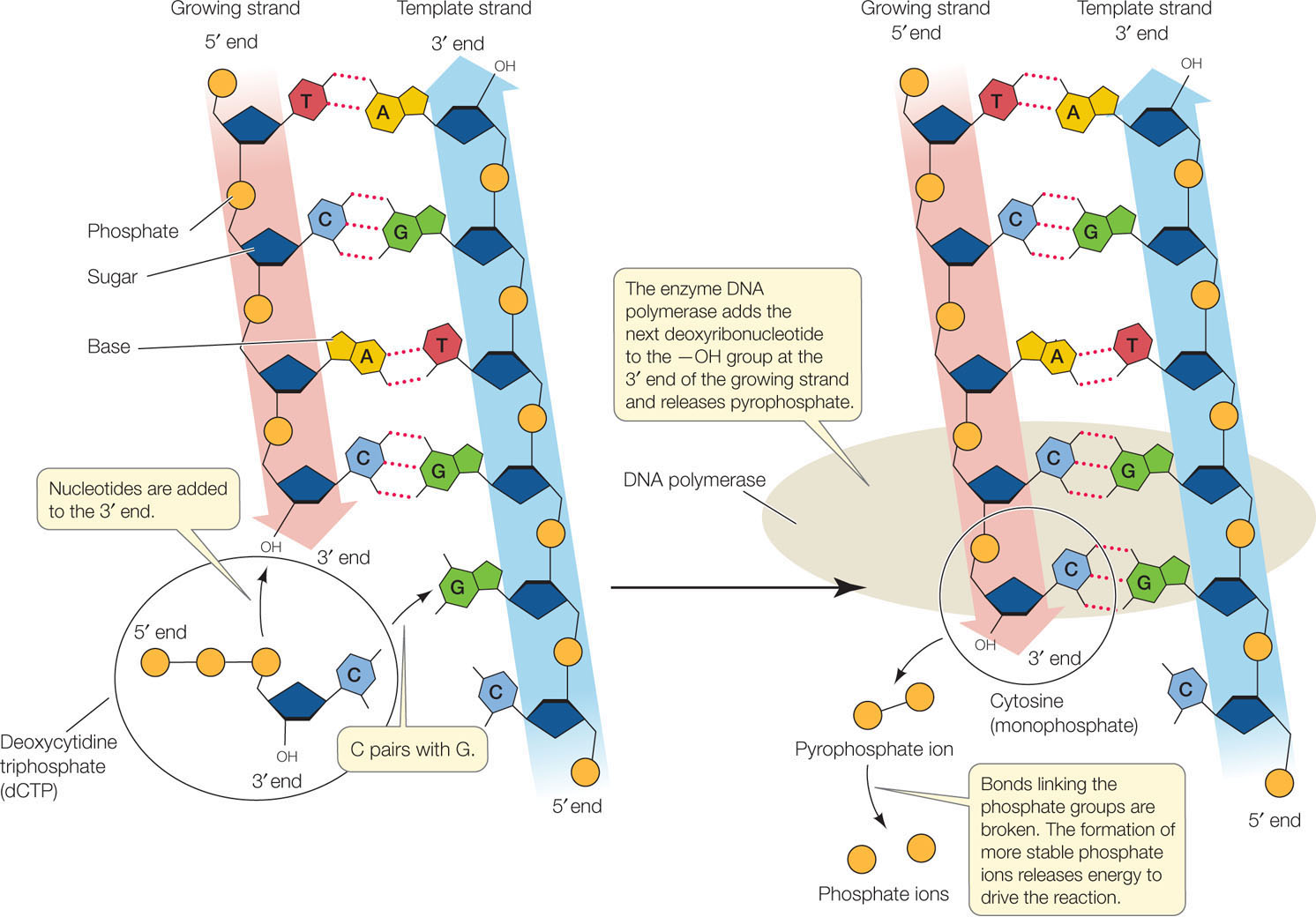
. The template strand specifies which of the four DNA nucleotides A T C or G is added at each position along the new chain. Cells must replicate their DNA before they can divide. The peptide then moves one codon position to get ready for the next amino acid.
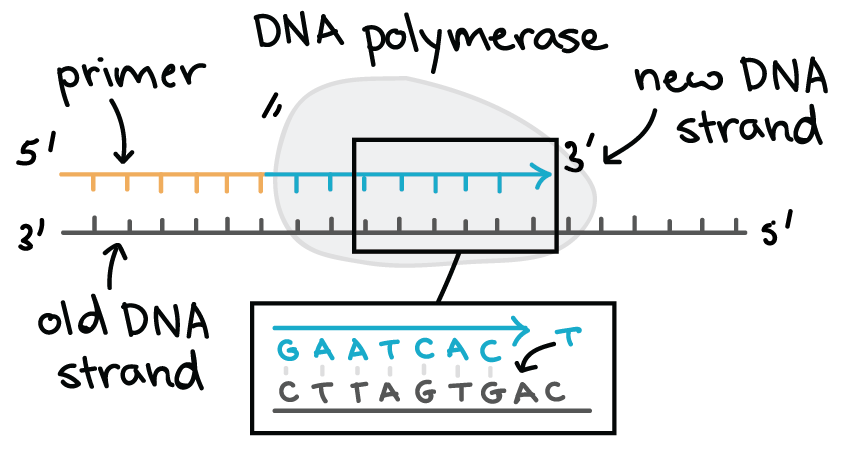
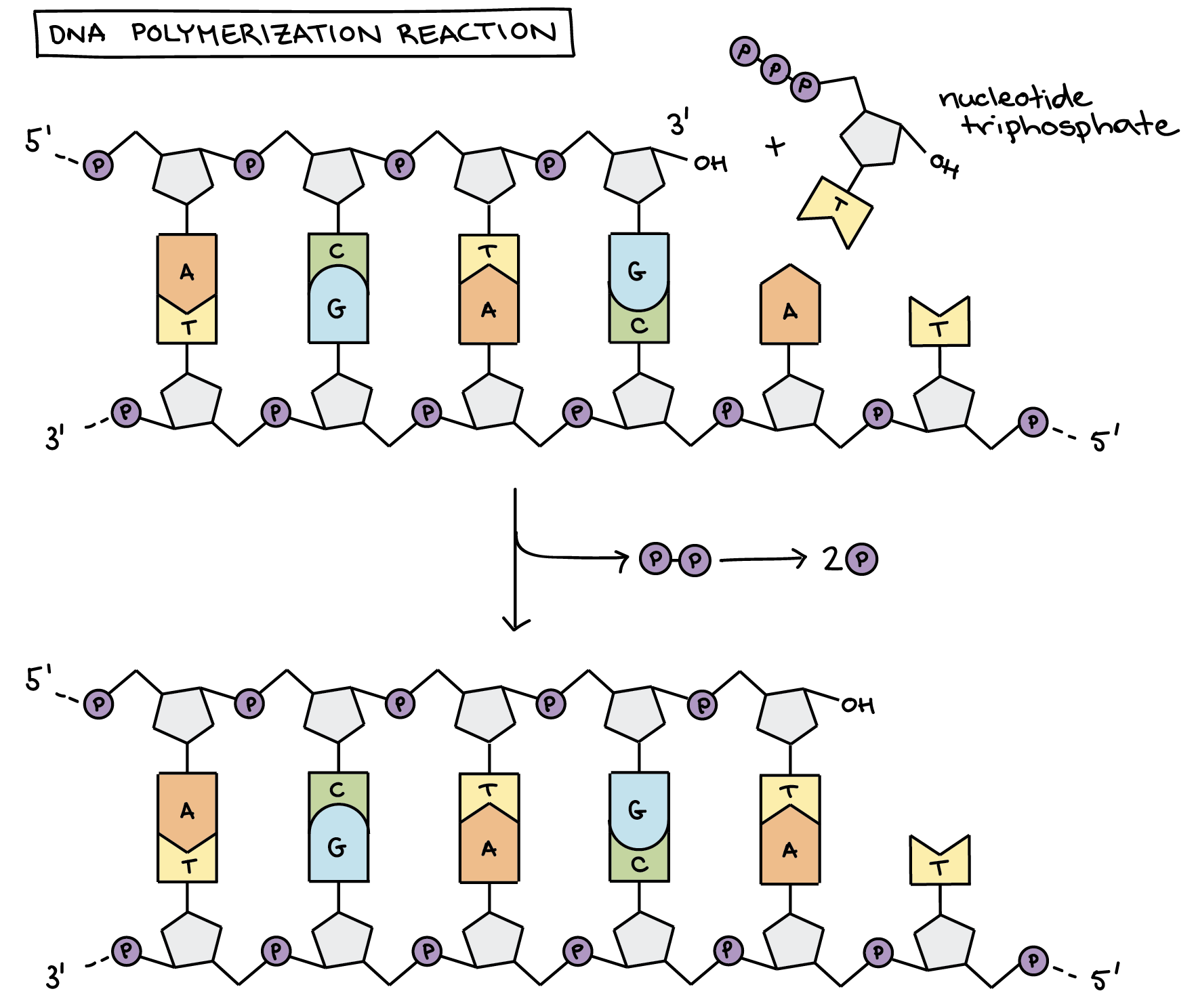
Each nitrogenous base of a DNA molecule provides a piece of information for protein. It catalyses the synthesis of DNA during replication. During elongation an enzyme called DNA polymerase adds DNA nucleotides to the 3 end of the newly synthesized polynucleotide strand.
Here rDNA is added to the recipient host cell and the entire process is called. Every codon encodes for just one amino acid but a given amino acid may be encoded by multiple codons. The figure shows the triplet code.
Insertion of rDNA into a Host. In biology transcription is the process whereby DNA is used as a template to form a complementary RNA strand RNA is the written form of DNA. Moreover its main function is to duplicate the DNA and divide in cell division.
DNA transcription is the process by which the genetic information contained within DNA is re-written into messenger RNA mRNA by RNA polymerase. Similar to the way DNA is used as a template in DNA replication it is again used as a template during transcription. List explain and apply the two basic tenets of Cell Theory.
It is a group of enzymes required for the synthesis of DNA. However the translation to protein is still systematic and colinear. Describe the structure of a polynucleotide.
Introduction to The Cell. Each codon consists of three consecutive RNA bases that together encode for one amino acid. The elucidation of the structure of the double helix provided a hint as to how DNA is copied.
Only the nucleotide complementary to the template nucleotide at that position is. In Eucaryotes DNA Replication Takes Place During Only One Part of the Cell Cycle. This mRNA then exits the nucleus where it acts as the basis for the translation of DNA.
This ensures that each daughter cell gets a copy of the genome and therefore successful inheritance of genetic traits. By controlling the production of mRNA within the nucleus the cell regulates the rate of gene expressionIn this article we will. The process of translation involves translating triplets of nucleotides called codons into the language of amino acids.
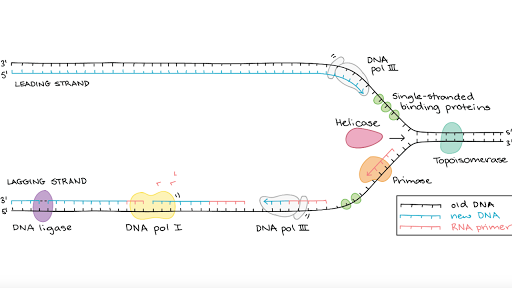
Either A T C or G. Sequence of nitrogenous bases and the template strand. During DNA replication inside a cell each of the two old DNA strands serves as a template for the formation of an entire new strand.
As a result this new hybrid DNA molecule is known as a recombinant DNA molecule and the process is known as recombinant DNA technology. When growing rapidly bacteria replicate their DNA continually and they can begin a new round before the previous one is complete. This means that the two strands are complementary to each other.
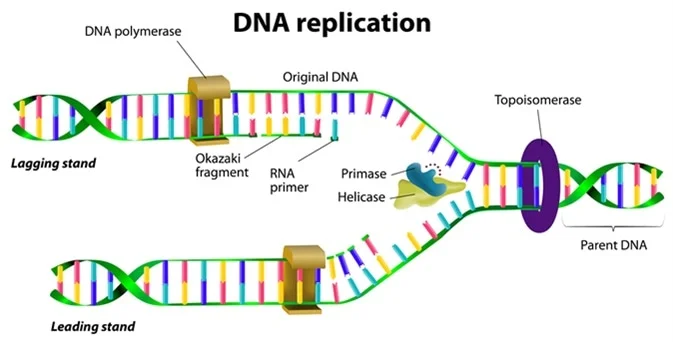
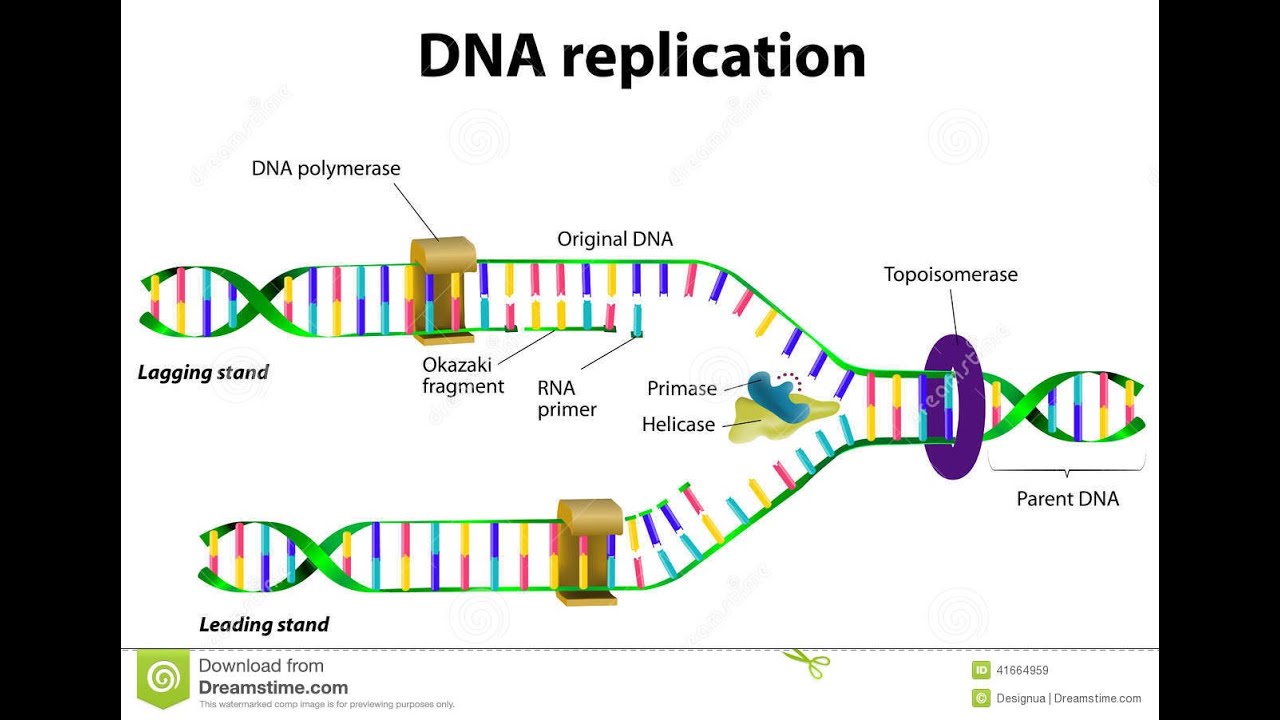
Unlike DNA synthesis which only occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle transcription and translation are continuous processes within the cell. Because each of the two daughters of a dividing cell inherits a new DNA double helix containing one old and one new strand Figure 5-5 the DNA double helix is said to be replicated semiconservatively by DNA polymerase. The primase generates short strands of RNA that bind to the.
Recall that adenine nucleotides pair with thymine nucleotides and cytosine with guanine. Each strand serves as a template for the DNA polymerase to catalyze the addition of the correct base during synthesis of a new complementary strand. DNA replication is an essential process and the basic mechanism is conserved in all organisms.
Recombination is the term used in genetics to describe the merging of different DNA strands. The replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis phase or S phase of the cell cycle before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis. DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter.
The helicase unzips the double-stranded DNA for replication making a forked structure. This is the first stage of protein production or the flow of information within a cell. This strand is called the leading strand.
At a temperature of 37 degrees Celsius new nucleotides are added at an estimated rate of about 42-54 nucleotides per second in bacteria Dennis. The information that is stored in DNA molecules is rewritten or transcribed into a new RNA molecule. DNA stores genetic information which is then transferred to RNA in transcription before directing the synthesis of proteins in translation.
Identify the 5 and 3 ends and describe how new nucleotides are added. The structure of DNA is dynamic along its length being capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes. In all species it is composed of two helical chains bound to each other by hydrogen bondsBoth chains are coiled around the same.
In contrast DNA replication in most eucaryotic cells occurs only during a specific part of the cell division cycle called the DNA synthesis phase or S phase Figure 5. The translation to protein is a bit more complex because three mRNA nucleotides correspond to one amino acid in the polypeptide sequence. There are various functionalities.
During translation the incoming aminoacyl t-RNA binds to the codon sequences of 3 nucleotides at A-site and a peptide bond is formed between the new amino acid and the growing chain. Identify the roles of covalent and hydrogen bonds in DNA structure and function. The process hence proceeds in a 5 to 3 direction.
9 2 Dna Replication Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
9 2 Dna Replication Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

Dna Replication And Repair Biol 230 Master Confluence

Rna Primer In Dna Replication Definition Function Sequence Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Chapter 14 Dna Replication In Fundamentals Of Cell Biology On Openalg
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
9 2 Dna Replication Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
9 2 Dna Replication Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

Dna Replication Steps Diagram Expii
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

Molecular Events Of Dna Replication Learn Science At Scitable

Dna Replication Flashcards Quizlet

Molecular Events Of Dna Replication Learn Science At Scitable


Comments
Post a Comment